Fireproof cleanroom doors are devices that ensure the airtight and dustproof standards of cleanrooms, while also being able to withstand heat and effectively prevent fire spread. Using fireproof cleanroom doors helps protect the safety of people and equipment and maintain compliance with GMP and ISO 14644 standards.
- 1. What is a Fire-Rated Cleanroom Door and Why is it Important?
- 2. Technical Standards for Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
- 3. Technical Structure of Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
- 4. Practical Applications and Installation Recommendations
- 5. Key Considerations When Selecting and Installing Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
- 6. Frequently Asked Questions
- 7. Need Help Choosing the Right Fire-Rated Cleanroom Door?
1. What is a Fire-Rated Cleanroom Door and Why is it Important?
A fire-rated cleanroom door is designed to ensure both air tightness and dust resistance according to cleanroom standards, while also being able to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire for a specific duration (typically EI30, EI60, or EI90). This type of door is crucial in areas with a high risk of fire or where strict fire safety control is required in manufacturing facilities.
Why are fire-rated doors necessary in cleanrooms?
In a cleanroom environment—where contamination control and compliance with standards such as ISO 14644 or GMP are mandatory—fire hazards can still occur due to:
- Heat-generating equipment (ovens, test chambers)
- Flammable materials (alcohols, solvents, chemicals)
- Electrical systems operating continuously
In such cases, a fire-rated cleanroom door acts as a safety barrier to:
- Prevent fire from spreading between clean zones
- Protect equipment, personnel, and stored materials
- Comply with fire safety and GMP inspection requirements
Common application scenarios:
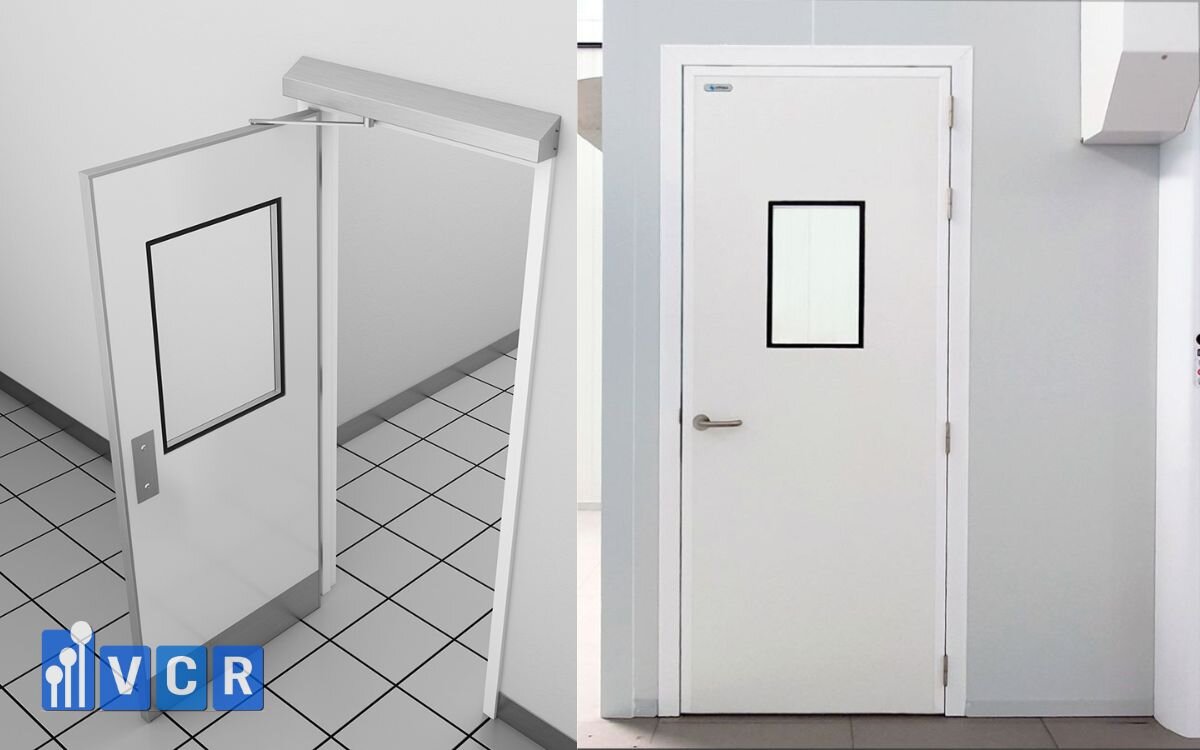

- Pharmaceutical industry: In weighing rooms or sample storage areas where flammable solvents like ethanol are used, fire-rated doors help prevent fire spread and cross-contamination during incidents.
- Food industry: In cooking or heating areas (boiling, frying, baking), doors must withstand high heat to protect adjacent areas like packaging or finished product storage.
- Electronics industry: In temperature test rooms or battery testing areas, fire-rated doors help minimize fire risk within sealed HVAC systems.
2. Technical Standards for Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
To ensure both fire resistance and compliance with cleanroom conditions, a fire-rated door must meet two groups of standards: fire resistance standards and cleanroom standards.
Fire Resistance Standards
The most common international and Vietnamese standards applied to fire-rated cleanroom doors include:
- EN 1634-1 (Europe): Defines fire resistance testing for doors at temperatures of 1,000-1,100°C. Results are expressed as EI ratings (e.g., EI30 = 30 minutes fire resistance).
- UL 10B/10C (United States): Evaluates fire and smoke resistance performance of metal and wooden doors. UL 10C applies to modern metal doors tested under positive pressure.
- TCVN 2622:1995 (Vietnam): Specifies fire prevention design requirements for buildings, including materials and minimum fire resistance times.
Fire-rated cleanroom doors typically come with certified fire test reports issued by authorized testing centers or fire safety organizations.
Cleanroom-Related Standards
In addition to fire resistance, the door must also meet cleanroom standards to maintain cleanliness levels and prevent contamination.
- ISO 14644-1: Defines air cleanliness classes from ISO Class 1 to ISO Class 9. Doors must be dust-free, smooth-surfaced, and airtight to maintain pressure differentials and airflow control.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice): In pharmaceutical and cosmetic facilities, GMP requires cleanroom systems to prevent cross-contamination, be easy to clean, and ensure fire safety.
→ Fire-rated doors must integrate seamlessly with interlock systems, pressure control, and anti-bacterial materials.
Common Fire Resistance Ratings (EI30, EI60, EI90)
The “EI” classification indicates:
- E (Integrity): Ability to prevent fire from penetrating through the door
- I (Insulation): Ability to prevent heat transfer through the door
The number (30/60/90) represents the maximum fire resistance duration in minutes.
|
Rating |
Fire Resistance Time |
Recommended Application |
|
EI30 |
30 minutes |
Low-risk areas, corridors, secondary doors |
|
EI60 |
60 minutes |
Weighing rooms, pharmaceutical production, chemical storage |
|
EI90 |
90 minutes |
Thermal testing labs, battery rooms, high-risk storage zones |
The appropriate EI rating should be determined based on:
- Installation location within the cleanroom layout
- Surrounding materials and equipment
- Internal fire safety and GMP audit requirements
See more: Latest price list of Clean room doors used in medical clean rooms
3. Technical Structure of Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
A fire-rated cleanroom door combines airtight, dust-resistant construction typical of cleanrooms with heat-resistant materials that prevent fire spread and protect people and equipment during emergencies. Its structure differs significantly from that of standard cleanroom doors.
Comparison: Standard vs. Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
|
Component |
Standard Cleanroom Door |
Fire-Rated Cleanroom Door |
|
Door Panel |
EPS or PU panel |
Mineral wool or Magnesium Oxide (MgO) fire-resistant core |
|
Observation Window |
Double-layer tempered glass |
Fire-resistant glass (EI30-EI60) with smoke-seal gaskets |
|
Door Frame |
Aluminum or lightweight alloy |
Galvanized steel or stainless steel with powder coating |
|
Hardware |
Standard hinges and locks |
Heavy-duty hinges, fire-rated locks, smoke-seal rubber gaskets |
|
Additional Features |
Basic soundproofing, easy cleaning |
Fire-resistant, airtight, pressure-resistant, easy to sterilize |
All components must ensure absolute airtightness and no particle emission, meeting ISO 14644 requirements without disrupting clean airflow.
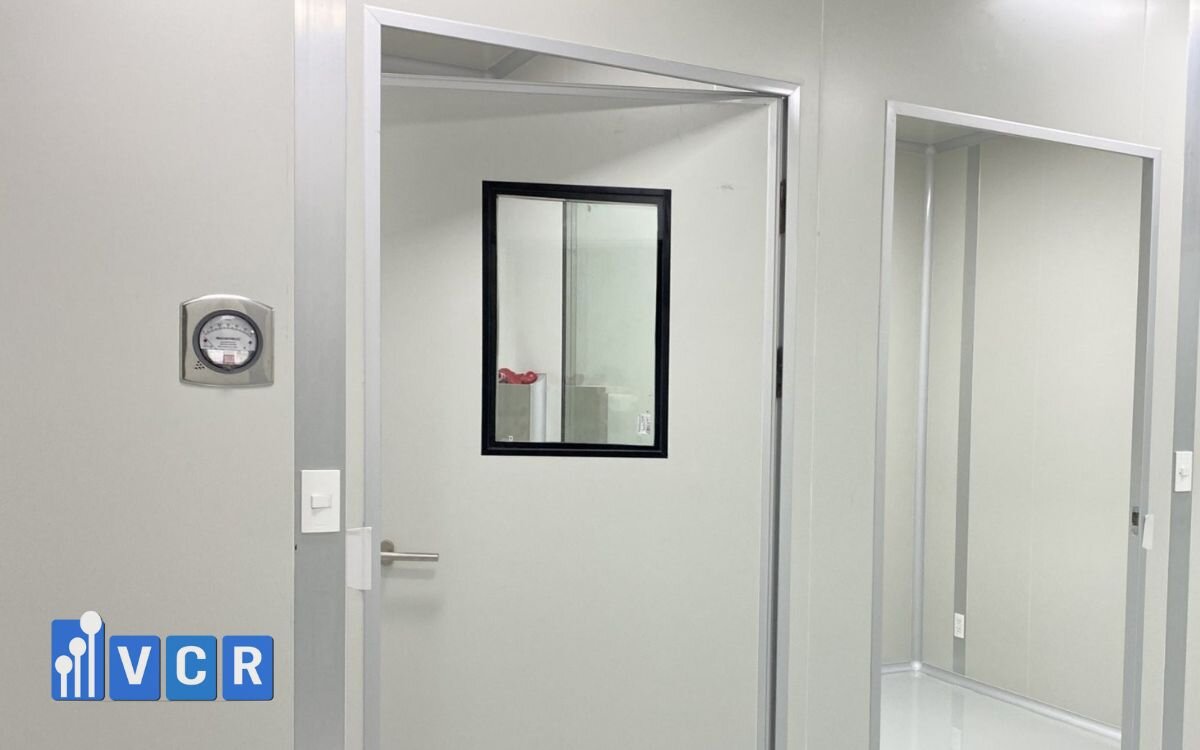

Configuration Options for Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
- Door Type:
- Single-leaf doors: Common in corridors or airlocks
- Double-leaf doors: Used in material transfer or wide-access zones
- Observation Window Options:
- With or without fire-rated glass
- Round or square shape, anti-fog and dust-sealed
- System Integration:
- Compatible with interlock systems, fire alarms, and pressure control systems
A properly designed fire-rated cleanroom door ensures not only fire safety but also stable cleanroom performance, supporting full compliance with GMP/ISO standards.
4. Practical Applications and Installation Recommendations
Not every location in a facility requires a fire-rated door. However, in areas with high fire risk or strict requirements for clean airflow control, installing a fire-rated cleanroom door is mandatory to ensure safety and compliance with GMP/ISO standards.
Recommended Locations for Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
Flammable material transfer areas
Example: Areas receiving solvents, alcohols, chemicals, or storing flammable raw materials
Objective: Prevent fire from spreading to production or packaging areas
Recommendation: Use EI60 or EI90 doors with small fire-rated glass and integrated interlock system
Between zones of different cleanliness levels
Example: From ISO 8 to ISO 5 areas, such as mixing rooms to weighing rooms
Objective: Maintain pressure differentials and prevent the spread of fire and smoke in case of incidents
Recommendation: Use fire-rated doors with airtight gaskets and automatic fire alarm system integration
Applications by Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
Weighing rooms handle flammable and sensitive materials like ethanol or acetone
Recommendation:
- Install EI60 fire-rated doors with a 3-door interlock system (airlock - weighing room - corridor)
- Combine with fail-safe electromagnetic locks, pressure sensors, and temperature alarms
Food Industry
Pre-processing and heating zones generate heat, grease, and involve high-powered electrical equipment
Recommendation:
- Use EI30-EI60 steel fire-rated doors between processing and packaging areas
- Prefer double doors with anti-fog observation windows, easy to clean
Tips for Designing Cleanroom Layouts
- Identify fire-risk areas early in the layout planning phase
- Select doors based on cleanliness class and required fire resistance time
- Integrate fire-rated doors with interlock and fire alarm systems for smooth operation
- Ensure emergency exits are equipped with EI60 or higher-rated doors on both ends
See more: Expert Guide to Cleanroom Steel Door Installation
5. Key Considerations When Selecting and Installing Fire-Rated Cleanroom Doors
Choosing the wrong type of door can impact cleanroom performance, pose fire hazards, and result in failure to meet GMP/ISO certification. Keep the following points in mind:
Select Products with Verified EN/UL Certification
Fire-rated doors must have valid fire test certificates from recognized organizations:
- EN 1634-1 (Europe)
- UL 10C (USA)
- Vietnam PCCC (fire safety) test report
Certificates should specify:
- Fire resistance duration (EI30, EI60, EI90)
- Material composition
- Testing agency name
Tip: Always request a scan of the certificate and a door label—especially for pharmaceutical or lab projects.
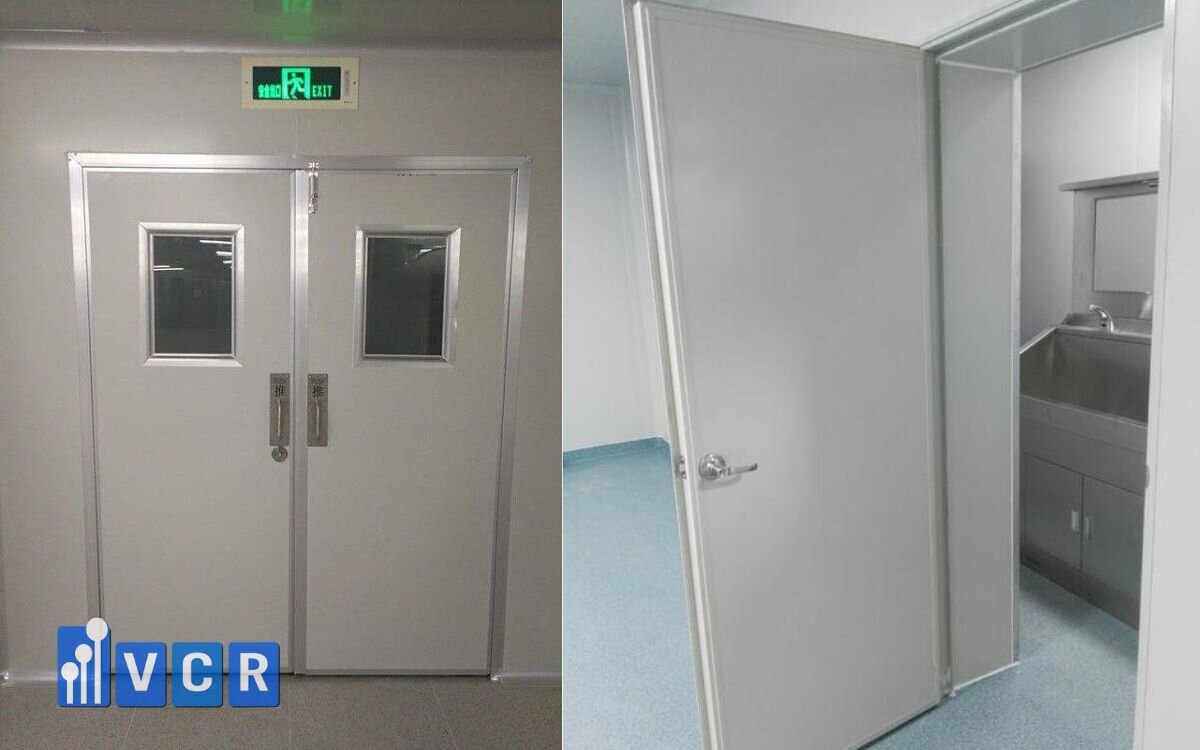

Match the Cleanroom Level and Heat Resistance Requirements
Each cleanroom zone has different needs:
- ISO 7-8 (pre-processing): EI30 may suffice
- ISO 5-6 (weighing, mixing): EI60 or higher recommended
Door materials must:
- Be dust-free and anti-static
- Resist corrosion and withstand cleaning chemicals
- Use gaskets that stay sealed even under heat
Coordinate with Interlock, Pressure Control, and Fire Alarm Systems
Fire-rated cleanroom doors must function as part of an integrated system:
Interlock System:
- Allows only one door to open at a time to prevent pressure loss
- Includes emergency release features
Pressure Sensors:
- Maintain positive or negative pressure between rooms as designed
Fire Alarm Integration:
- Doors auto-open or close depending on escape route protocols
- Locks must be fail-safe or support fire-priority control
Routine Maintenance is Essential
Even certified doors can degrade after 12-24 months without proper checks.
Maintenance checklist (every 6 months):
- Inspect rubber gaskets: Are there cracks, hardening, or deformation?
- Check hinges and locks: Any sticking, wear, or door sagging?
- Surface condition: Signs of corrosion or peeling?
- EI glass panel: Still clear? Any cracks?
See more: When to invest in automatic doors in clean rooms?
6. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is an EI60 fire-rated door required for an ISO 7 cleanroom?
It depends on the installation location and fire risk. If the door is near a heating area, weighing room, or solvent handling zone, EI60 is recommended to enhance safety and meet GMP/fire code requirements. For low-risk areas like corridors, EI30 may suffice.
2. Can a wooden fire door be used in a cleanroom?
Not recommended. While some wooden doors are fire-rated, they are not suitable for cleanroom use because:
- Wood emits particles and is prone to mold
- Difficult to clean and does not offer smooth, sealed surfaces
- Fails to meet ISO 14644 and GMP cleanliness requirements
Preferred materials include powder-coated steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloys.
3. Can interlock systems be integrated with fire-rated doors?
Yes. Fire-rated doors can be integrated with interlock systems if:
- Fire-certified hardware is used
- The system includes a fail-safe mode in case of power loss or fire alarm
- Custom control panels are designed for fire-critical areas
This is ideal for weighing rooms, airlocks, or zones with strict cleanliness zoning.
7. Need Help Choosing the Right Fire-Rated Cleanroom Door?
Choosing the right door not only affects cleanroom control but also ensures fire safety compliance and successful GMP/ISO inspections.
Are you unsure whether to choose EI30, EI60, or EI90?
Do you want a door integrated with interlock and fire alarm systems?
Do you need certified documentation for audit approval?
Let VCR’s technical team support you with:
- Cleanroom layout and fire risk analysis
- Door configuration recommendations for each area
Hotline: 090.123.9008
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://cuaphongsachvcr.com/
Diep VCR